Urine Incontinence Homeopathy Treatment in Chennai
- Dr Sheela Homeopathy Clinic Chennai
- Apr 21, 2025
- 7 min read
#urineincontinencehomeopathy #urineincontinencehomeopathyclinic #urineincontinencehomeopathytreatment #urineincontinencehomeopathydoctorinchennai #urineincontinencehomeopathicclinicinchennai #urineincontinencehomeopathictreatmentinchennai #urineincontinencehomeopathyclinicintambaram
Urinary Incontinence Homeopathy Treatment in Chennai Urine incontinence Homeopathy Treatment in Chennai
Urinary Incontinence Homeopathy Clinic in Chennai
Urine incontinence, a common yet often embarrassing condition, affects millions of people worldwide, both men and women of all ages. Urine incontinence is a condition that many people struggle with but often avoid discussing due to embarrassment or social stigma. It refers to the involuntary leakage of urine, which can vary in severity and impact daily life in different ways. While it may be seen as a normal part of aging, urine incontinence is not a natural consequence of getting older, and there are effective treatments available to manage and even resolve it.
What is Urine Incontinence?
Urine incontinence refers to the involuntary release of urine from the bladder. It occurs when there is a dysfunction in the normal process of urine storage and release. Normally, the bladder fills with urine from the kidneys, and when it reaches a certain level of fullness, nerve signals are sent to the brain to indicate the need to urinate. At this point, the brain sends signals to the bladder muscles (detrusor muscle) to contract and to the sphincter muscles to relax, allowing urine to be released through the urethra.
However, in people with urine incontinence, one or more factors in this process do not function properly, leading to the involuntary loss of urine. This condition can range from mild leakage to a complete loss of bladder control.
Urine incontinence can be temporary or chronic, and it can occur at any age, although it becomes more common with age, particularly among women. It is not a disease in itself but a symptom of underlying conditions or dysfunctions in the urinary system.
Pathophysiology of Urine Incontinence
The urinary system relies on the coordinated interaction of the bladder, urethra, sphincter muscles, and the brain for normal function. The key components involved in bladder control are:
Bladder: A hollow organ that stores urine produced by the kidneys. The bladder stretches as it fills with urine and contracts when it's time to urinate.
Detrusor Muscle: A smooth muscle that makes up the walls of the bladder. It contracts to expel urine when the bladder is full.
Sphincter Muscles: These muscles (internal and external) control the opening and closing of the urethra, preventing urine from leaking out until it’s time to urinate.
Nervous System: The brain communicates with the bladder through a network of nerves to control the contraction and relaxation of the detrusor and sphincter muscles.
In healthy individuals, the detrusor muscle remains relaxed while the bladder fills. When the bladder reaches a certain fullness, nerve signals trigger the detrusor muscle to contract, pushing urine into the urethra. Simultaneously, the sphincter muscles relax, allowing urine to pass.
Urine incontinence occurs when there is a disruption in this normal process. This can be caused by issues with the bladder muscles, nerve signals, or sphincter muscles. In some cases, external factors like pressure on the bladder (e.g., during pregnancy) or an obstruction (e.g., an enlarged prostate) can also interfere with normal bladder function.
Types of Urine Incontinence
Urine incontinence is not a single condition but rather a collection of types that can result from different causes and mechanisms. Here are the most common types of urinary incontinence:
1. Stress Incontinence
This type occurs when there is pressure on the bladder, such as during physical activities like coughing, sneezing, laughing, lifting heavy objects, or exercise. The pressure overwhelms the bladder’s sphincter muscles, causing urine to leak. Stress incontinence is more common in women, especially after childbirth or menopause, but it can also affect men, particularly after prostate surgery.
2. Urge Incontinence (Overactive Bladder)
Urge incontinence is characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate, often followed by involuntary leakage of urine. This happens when the detrusor muscle contracts involuntarily, causing an urgent need to urinate. People with urge incontinence may experience frequent urination, including waking up several times during the night to urinate. It is common in older adults but can affect younger individuals as well.
3. Overflow Incontinence
Overflow incontinence occurs when the bladder doesn’t empty completely, leading to the constant or frequent leaking of small amounts of urine. It is usually caused by a blockage or weak bladder muscles that prevent the bladder from emptying fully. This can result in a constant dribbling of urine or the sudden release of large amounts of urine. It can happen in both men and women but is more common in men with prostate problems.
4. Functional Incontinence
This type of incontinence occurs when physical or mental impairments prevent an individual from reaching the bathroom in time. Conditions like arthritis, severe dementia, or mobility problems can interfere with the ability to get to the bathroom and initiate urination, even if the bladder itself is functioning normally.
5. Mixed Incontinence
Mixed incontinence is a combination of more than one type of urinary incontinence. Most commonly, it refers to a mix of stress incontinence and urge incontinence. Individuals with mixed incontinence may experience both the leakage triggered by physical activity (stress incontinence) and the urgent, uncontrollable urge to urinate (urge incontinence).
6. Nocturnal Incontinence (Bedwetting)
This type of incontinence occurs when an individual involuntarily urinates while sleeping. While it is common in children, it can also affect adults. Nocturnal incontinence may be due to an overactive bladder, hormonal imbalances, or even sleep disorders.
Causes of Urine Incontinence
The causes of urine incontinence vary greatly depending on the type and individual factors. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Pregnancy and Childbirth
In women, pregnancy and childbirth can weaken the pelvic floor muscles and damage the nerves that control bladder function, leading to stress incontinence. The pressure exerted by the growing fetus on the bladder during pregnancy can also contribute to incontinence.
2. Aging
As people age, the muscles that control the bladder can weaken, leading to problems with urine control. In addition, older adults may experience other factors such as enlarged prostate (in men) or changes in hormone levels that contribute to incontinence.
3. Neurological Conditions
Conditions that affect the nervous system, such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or spinal cord injury, can disrupt the communication between the bladder and the brain, leading to urinary incontinence.
4. Prostate Problems
In men, an enlarged prostate or prostate surgery (such as a prostatectomy) can lead to overflow incontinence. The prostate’s location near the bladder and urethra means that any issues with it can interfere with normal bladder function.
5. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs can cause urinary incontinence, particularly urge incontinence, because the infection irritates the bladder, making it more sensitive and prone to involuntary contractions.
6. Medications
Certain medications, such as diuretics (used to treat high blood pressure), can increase urine production, which can lead to temporary incontinence. Other drugs, like sedatives or antidepressants, may also affect bladder function.
7. Hormonal Changes
For women, changes in hormone levels during menopause can reduce the strength of the pelvic floor muscles and contribute to stress incontinence. Hormonal fluctuations can also affect bladder control.
8. Obesity
Being overweight or obese increases the pressure on the bladder, which can weaken the pelvic floor muscles and contribute to both stress and urge incontinence.
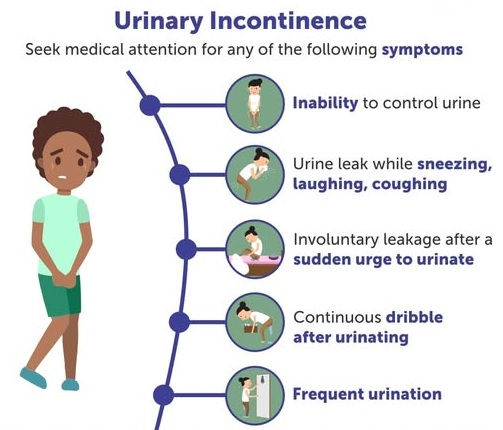
Symptoms of Urine Incontinence
The symptoms of urine incontinence depend on the type of incontinence but generally include:
Frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturnal).
Urgency to urinate, often with an inability to reach the bathroom in time.
Involuntary urine leakage when laughing, sneezing, coughing, or exercising.
A feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after urination.
Small or continuous dribbling of urine.
Frequent UTIs due to urine retention.
Complications of Urine Incontinence
Urine incontinence can lead to several physical, emotional, and social complications, such as:
Skin problems: Persistent leakage can cause skin irritation or rashes.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Incontinence can increase the risk of UTIs, especially if hygiene is not maintained properly.
Emotional distress: Many people with incontinence feel embarrassed, anxious, or depressed, which can impact self-esteem and quality of life.
Sleep disturbances: Waking up frequently at night to urinate can lead to disturbed sleep, resulting in fatigue and daytime drowsiness.
Social isolation: People with incontinence may avoid social gatherings, travel, or other activities due to fear of embarrassing accidents.
Common Urinary Bladder Problems in Adults:
Here are some common urinary bladder problems in adults include:
1.Frequent urination
2.Rushing to the bathroom
3.Wetting accidents
4.Trouble urinating
5.Dribbling after urinating
6.Urinary tract infections
7.Burning or discomfort before and after urination
8.Occasionally blood in the urine which could be pinkish tinge or bright red.
Urine Incontinence homeopathy treatment in Chen
Urinary Incontinence homeopathy treatment in Chennai.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Urinary Incontinence
a) Who is at risk for urinary incontinence?
Women, especially those who have been pregnant or have given birth, are at a higher risk, as are older adults, people with certain chronic conditions (like diabetes or neurological disorders), and individuals with obesity.
b) Can urinary incontinence be a sign of another medical condition?
Yes, urinary incontinence can sometimes be a symptom of underlying conditions such as bladder infections, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, stroke, or multiple sclerosis. It is important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis if you experience sudden or severe incontinence.
c) Does weight loss help with urinary incontinence?
Yes, losing excess weight can relieve pressure on the bladder and pelvic muscles, which can reduce the frequency or severity of urinary incontinence. For some people, losing just 5-10% of body weight can make a noticeable difference.
d) How does menopause affect urinary incontinence?
During menopause, hormonal changes can lead to a decline in estrogen, which can weaken the tissues of the bladder and urethra. This can contribute to urinary incontinence, especially stress incontinence. Pelvic floor exercises and other treatments may help manage this.
e) Can urinary incontinence affect my social life?
Yes, urinary incontinence can impact daily life and social activities, causing embarrassment and limiting social interactions. However, there are treatments and products available that can help manage symptoms and restore confidence. Speaking to a healthcare provider can help you find the best options for your situation.
f) What are the risks of untreated urinary incontinence?
Untreated urinary incontinence can lead to complications such as skin irritation, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and emotional distress like anxiety or depression. Chronic incontinence can also lead to reduced quality of life and physical limitations.